Creating a successful e-commerce website involves several key steps, from domain registration to integrating a payment gateway. Here’s a detailed breakdown of each phase:
1. Domain Registration
Choosing a Domain Name
- Relevance: Choose a name that reflects your business or brand. It should be easy to remember and spell.
- Availability: Use domain registration services like GoDaddy, Namecheap, or Google Domains to check if your desired domain is available.
- Extensions: Common extensions include .com, .net, .org, but there are many others like .shop, .store, which can be more specific to e-commerce.
Registering the Domain
- Selection: Once you find an available domain, proceed to register it through a registrar service.
- Duration: You can register a domain for a period ranging from one to ten years. Many registrars offer discounts for longer-term registrations.
- Privacy: Consider adding domain privacy protection to keep your personal information private from the public WHOIS database.
2. Types of Hosting
Shared Hosting
- Description: Multiple websites share the same server and resources.
- Pros: Cost-effective, easy to set up, suitable for small to medium-sized websites.
- Cons: Limited resources, can be slower, less control over server settings.
VPS (Virtual Private Server) Hosting
- Description: A server is divided into virtual servers, each acting as an independent server.
- Pros: More control and resources compared to shared hosting, better performance, scalability.
- Cons: More expensive than shared hosting, requires technical knowledge.
Dedicated Hosting
- Description: Entire server dedicated to a single website.
- Pros: Maximum control, high performance, best for large websites with high traffic.
- Cons: Expensive, requires technical expertise to manage.
Cloud Hosting
- Description: Uses a network of servers to host websites, offering scalability and redundancy.
- Pros: Highly scalable, reliable, pay-as-you-go pricing.
- Cons: Can be complex to manage, costs can add up with high usage.
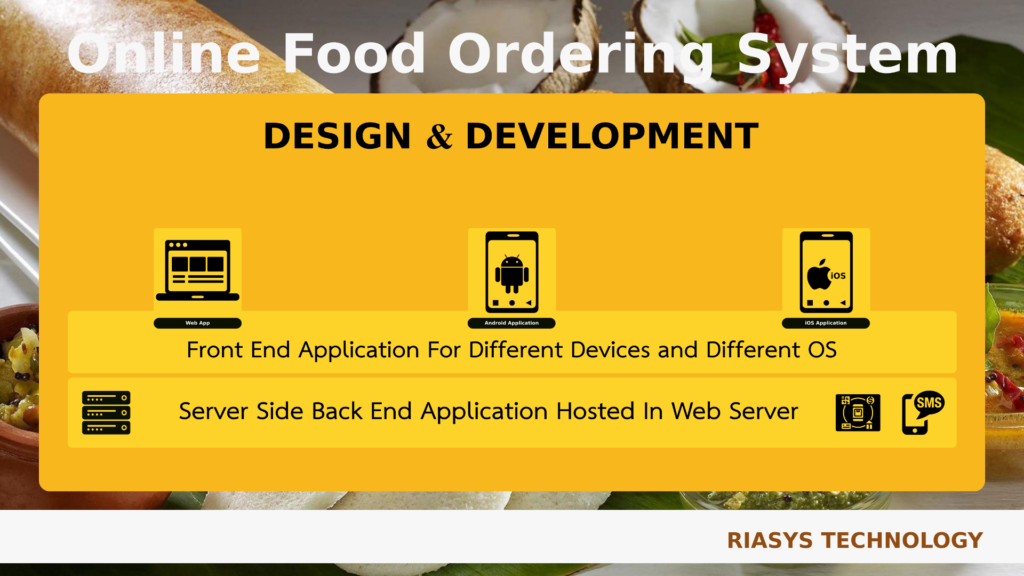
3. Design and Development
Planning and Research
- Target Audience: Identify who your customers are and what they need.
- Competitor Analysis: Look at competitors to understand what works and what doesn’t.
- Feature List: Decide on essential features like product categories, search functionality, user accounts, and reviews.
Design
- Wireframing: Create wireframes to outline the structure and layout of the site.
- Mockups: Develop visual designs and mockups using tools like Adobe XD, Sketch, or Figma.
- Responsive Design: Ensure the design is responsive and works well on all devices, including mobiles and tablets.
Development
- Choosing a Platform: Select an e-commerce platform like Shopify, WooCommerce (for WordPress), Magento, or custom development.
- Frontend Development: Implement the design using HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and frameworks like React or Vue.js.
- Backend Development: Develop the server-side functionality using languages like PHP, Node.js, or Python. Set up a database using MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB.
Integration
- Content Management System (CMS): Integrate a CMS for easy content updates.
- Inventory Management: Implement inventory management systems to track stock levels.
- SEO: Optimize the website for search engines to improve visibility.
4. Payment Gateway Integration
Choosing a Payment Gateway
- Popular Options: PayPal, Stripe, Square, Authorize.net, and local payment solutions depending on the target market.
- Transaction Fees: Compare transaction fees and terms of service.
- Supported Currencies: Ensure the gateway supports the currencies you need.
Integration Process
- API Documentation: Follow the payment gateway’s API documentation for integration.
- Security: Implement SSL certificates to secure transactions. Ensure compliance with PCI-DSS standards.
- Testing: Use sandbox environments provided by the payment gateway to test transactions before going live.
- User Experience: Make the checkout process smooth and intuitive to reduce cart abandonment rates.
5. Testing and Launch
Testing
- Functionality Testing: Ensure all features work as intended.
- Performance Testing: Check the website’s speed and performance under various conditions.
- Security Testing: Conduct security audits to identify and fix vulnerabilities.
- Usability Testing: Get feedback from real users to improve the user experience.
Launch
- Final Checks: Perform final checks to ensure everything is ready.
- Marketing: Plan and execute marketing strategies for launch, including SEO, PPC, and social media campaigns.
- Monitoring: Use analytics tools to monitor website traffic and user behavior, and make data-driven decisions for improvements.
Conclusion
Developing an e-commerce website involves careful planning and execution across multiple stages. From choosing the right domain and hosting solution to designing a user-friendly interface and integrating secure payment gateways, each step is crucial for building a successful online store. By following these detailed steps, you can create an efficient, secure, and customer-friendly e-commerce platform that drives sales and growth for your business.